Definition of objectives and kpis
Key role(s)
Objectives
Benefits
Defining KPIs starts with the definition of objectives and key success factors and ends with the definition of the measures to be taken to calculate the metrics that will give the KPIs.
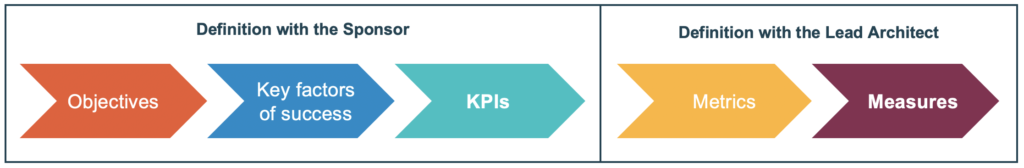
The part on the left (objectives, key success factors and KPIs) are to be defined with the sponsor. While the choice of metrics and measures to be implemented will be to be defined with the Lead Architect.
For the KPIs, we won't forget to :
- Define IT metrics to measure IT efficiency (such as average cost per GB of storage, or average cost per hour of compute...).
IT KPIs (examples)
- Tagging coverage rate
- Costs per compute hour
- Costs per GB of storage
- Utilization rate of Reserved Instances
- Utilization rate of total Instances
- Utilization rate of storage volumes
- But also define indicators per business unit to measure the impact on company-specific elements that affect margins. The evaluation of success is not limited to IT cost efficiency, but to the positive impact on the business.
Business KPIs (examples)
- Actual spend vs committed spend
- Costs per business unit vs planned
- Costs per transaction vs planned
- Transactions number vs planned
- Costs per user vs planned
- % savings over the period
The different objectives of KPIs

We can therefore ask ourselves the questions around its 4 objectives in order to define the appropriate KPIs.
For example: Which KPIs would allow us to justify the refactoring actions we are considering for solution A?
Set up indicators
Setting up a KPI is not free, there are a certain number of steps to take into account and it is therefore important to ask yourself the right questions at the beginning so as not to waste time and money by trying to avoid wasting it!
- Step 1: Start by defining the need: what are we trying to find, justify, validate?
- Step 2: Then define the frequency and method of collection.
- Step 3: Determine and set up the necessary tools (with the tools we already have? By hand? With new tools? And of course by estimating the additional cost.
- Step 4: Write the procedures to perform these tasks (which can be 100% automated or on the contrary 100% manual) and write the code if necessary.
- Step 5: Validate the solution: won't it be counterproductive? Dangerous for perfumes, expenses? Does it meet the needs?
- Step 6: Start the collection