Reporting & Billing
Key role(s)
Objectives
Benefits
Bill of IT
Billing involves, in particular, the production of a "Bill of IT" that puts IT costs into perspective in relation to business data.
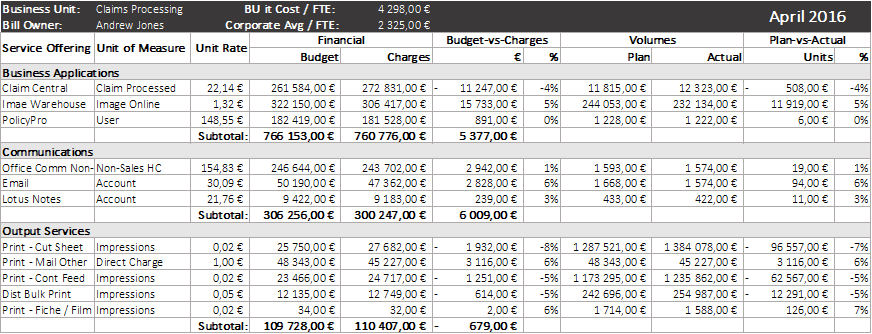
In this example, the costs associated with a BU are given by application :
- the "business" unit of measure for the costs,
- the "price" per unit,
- budget, actual and change
- but also, and this is the point, the forecast and actual volumes and their variation.
So when spending is up over budget you can see the direct correlation. If for example the costs of an application are 10% over budget but the volumes correspond to the plan, then we have an increase in the unit price... We will have to investigate further on this application.
Unit Rate
You may already have a very clear vision of the cost per unit of measurement for an application, but if this is not the case, you have to start from assumptions and move forward iteratively.
For example: We start by estimating, in relation to the initial infrastructure, the overall monthly cost of the application. Based on the information available or by requesting an estimate from the relevant BU, the volume is estimated (e.g. how many transactions per month are expected) and then the unit rate is calculated by dividing the estimated cost by the volume estimate. But it is well known that it is not that simple, there are fixed costs, which means that if volumes decrease the costs will not decrease proportionally and therefore the unit rate will increase. But the more we do the exercise, the more reliable we will be, especially if we constantly try to reduce the share of fixed costs.
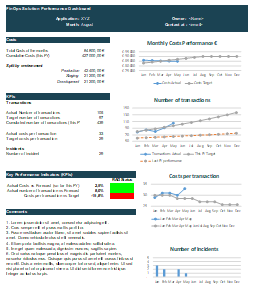
Reporting
Finally, thanks to the tools available or spreadsheets, it will be possible to set up reporting and even dashboarding to give the sponsor and the business units a good understanding of consumption and the actions to be carried out as a priority.